Do you wonder why you’re getting so little traffic from the search engines? Why Google ranks your competition higher than you? This 13 point SEO checklist will help you navigate your way to page one.
 Lately I’ve been reviewing a number of business websites that seem to be ignoring SEO completely. Now, obviously, the reason I’m reviewing these sites is because they’ve reached out to flyte because they feel like their website isn’t working and they want to know why.
Lately I’ve been reviewing a number of business websites that seem to be ignoring SEO completely. Now, obviously, the reason I’m reviewing these sites is because they’ve reached out to flyte because they feel like their website isn’t working and they want to know why.
So, they know something is wrong.
And just because their SEO is non-existent doesn’t mean that’s the only hurdle to generating more leads at their website, but it is a critical piece.
So, if you feel like your SEO isn’t working, maybe it’s time to take a look at the basics…at least the basics as they stand today.
Needless to say, this isn’t everything you can be doing to improve your chances of beating your competition at the search engines. There’s plenty of advanced SEO tactics we’ll save for another day, like schema, rich snippets, and externalizing JavaScript and CSS.
Measuring Tools
There are an infinite number of tools you can employ to measure your search engine visibility and success. These two are both essential and free.
1. Google Analytics
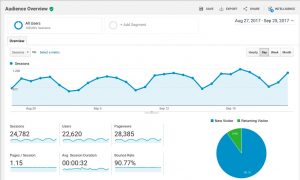 If you don't have Google Analytics installed, you can't measure your site traffic.
If you don't have Google Analytics installed, you can't measure your site traffic.
If you don't regularly read and analyze your Google Analytics, then you have no idea how people are finding your site, what they're doing when they get there, and if they're taking desired actions on your site.
Running your business website without Google Analytics is like archery in the dark: you have no way of knowing if you're hitting your target.
Solution: Make sure you set up Google Analytics…the right way.
2. Search Console
Formerly called Webmaster Tools, Search Console can be accessed on its own or connected to Google Analytics to unlock a lot of SEO related reports.
As Google has moved away from giving you all the information you want about specific keywords, Search Console has become a critical tool in understanding what search terms you're ranking for, at what (average position), and what percentage of your views are turning into clicks and visitors.
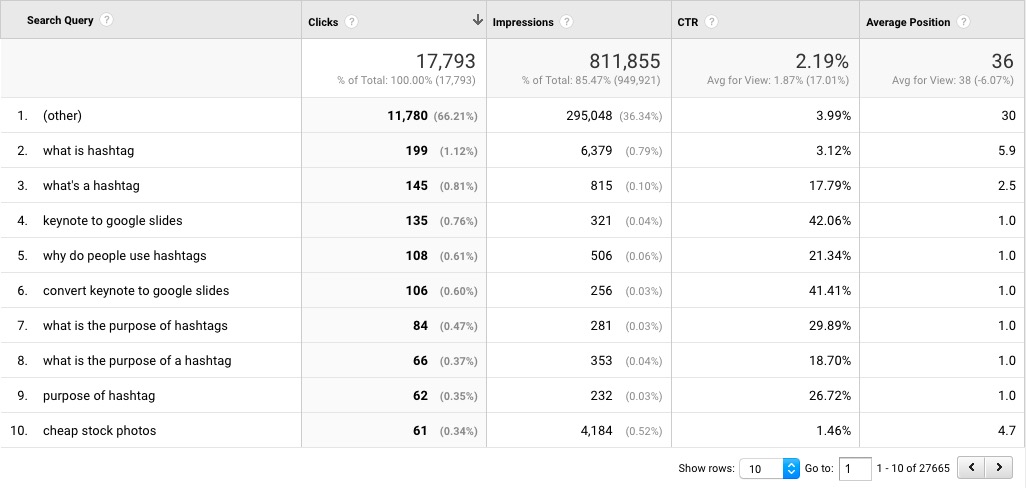
Solution: Connect Search Console to your Google Analytics.
Technical Aspects Affecting Your SEO
There are a lot of technical aspects that can impact the search engines' ability to access, review, and rank your site. Let's focus on three big ones that have a lot of impact today.
3. Are You Mobile-Friendly?
With more than half of the world's internet traffic arriving on a mobile device, it makes good business sense that your website is mobile-friendly.
It also makes good SEO sense. Google is now punishing sites that don't offer a mobile-friendly version, at least in mobile search. If your website isn't mobile-friendly, it's less likely to get found.
What makes a website mobile-friendly? If you have to pinch, double-tap, zoom, stretch, or rotate your website, chances are its not mobile friendly. There are several ways to make your website mobile-friendly, but probably the most “future-proof” way currently is called Responsive Web Design, or RWD.
Responsive design ensures that your website is optimized regardless of the size screen your visitor is using, and it's becoming a bigger variable in your search rankings all the time.
Solution: Make sure you're running a mobile-friendly website.
4. Do Your Pages Load Quickly?
Site speed is becoming a bigger and bigger issue when it comes search engine rankings. This probably goes to Google's desire to promote sites that provide a positive experience for users. A slow-loading page doesn't.
Back when I first started developing websites, we cared a lot about site speed, in part because most people were still using dial-up modems! And to get on the web we had to walk a mile in the snow. Uphill…both ways!
But as people got faster connections to the internet, a lot of web developers stopped worrying as much about load time. However, many people still have slow connections, and when people are on a mobile device, they're victim to the network they're on.
The good news is that Google provides a report that will tell you what you need to do to speed up the pages on your site. Whether it's optimizing images, reducing bloated code, etc.

Solution: Run Google PageSpeed Insights (also available through your analytics) and make the changes!
5. Is Your Site Secure?
![]() Is your site on https or just http? It used to be that only e-commerce sites and sites that captured secure information needed to be encrypted with https, but now Google has told us that it's a ranking factor. Now, it might be a minor ranking factor today, but it is likely to increase in importance as time goes on.
Is your site on https or just http? It used to be that only e-commerce sites and sites that captured secure information needed to be encrypted with https, but now Google has told us that it's a ranking factor. Now, it might be a minor ranking factor today, but it is likely to increase in importance as time goes on.
Solution: Get an SSL certificate for your site! (You can generally get one through your host, registrar, or with the help of your web development company.)
On Page Optimization Items
These are things that people see when they visit your website, and search engines pay particular attention to them. This assumes that you've done some sort of keyword analysis already or hired an SEO agency to help uncover your best keywords.
Now, if you've been paying attention, both Google and many SEO experts have been downplaying the importance of keywords lately. What Google wants you to do is stop focusing entirely on keywords and focus on creating valuable content for your visitors…and SEO experts have followed suit in their recommendations.
However, understanding the words your customers use at Google and other search engines–a.k.a., keyword research–is incredible important to creating that valuable content! Your customers want to know that you're speaking the same language, so keyword analysis is a critical step.
Once that's been done, it's about putting those keywords into the right places.
6. Start with your Title Tags
Title tags actually appear outside your web pages. They show up in the title bar or in the browser tabs.
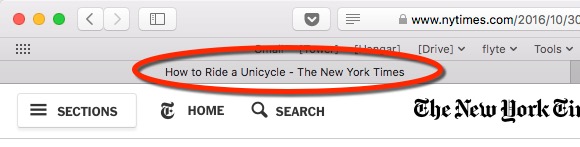
They're also the big blue links at the search engines.
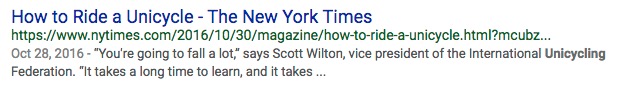
According to Search Engine Watch, title tags should be between 50 – 60 characters in length and should start with your best keywords. If your page is about chainsaw juggling, then Chainsaw Juggling should start your page title.
If you're using a content management system like WordPress, you can enter the title of your page while in the edit mode, or use an SEO plugin like Yoast for even more control.
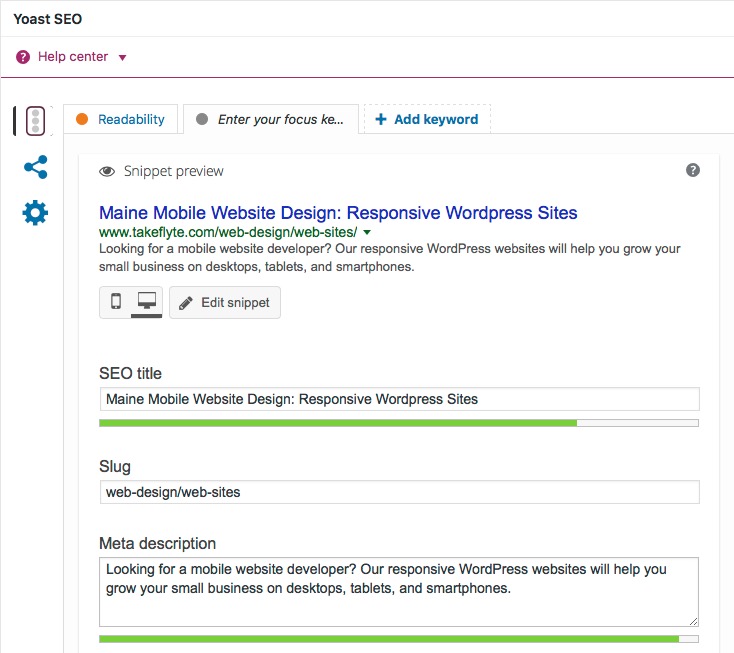
Solution: Review your page titles across your website. Make sure they are the right length, begin with your targeted keywords, and are in concert with the content on that page. Every page deserves a unique title tag.
7. Leverage your meta-descriptions.
Meta-descriptions don't actually show up on your web page. Rather, they are a description in the code that says what the page is about. These should not be confused with meta-keywords, which have been ignored by the search engines since about 1997. These days, meta-descriptions are often the black text you see under the big blue links at the search engines.
According to Moz, your meta-description can be any length, but generally gets cut off at 160 characters. While the meta-description has little to no direct value in terms of how well you rank, a well-written meta-description can convince a searcher to choose you instead of another result on the page.
Consider your meta-description as a short ad to persuade someone to visit your site. You can even include your phone number. Remember: if someone is searching on a mobile device, that phone number becomes a clickable link!

Solution: Using a tool like Yoast, review and optimize your meta-descriptions for keywords and length. Includes calls-to-action and a phone number as appropriate.
8. Use Headers and Subheaders
Headers and subheaders help break up your copy into scannable bits. That's good for humans. However, they also emphasize what your page is about. That's good for search engines.
If you know HTML, headers are usually defined within <h1> or <h2> tags, although they can go all the way down to <h6>. If you have no idea what I'm talking about, “8. Use Headers and Subheaders” above is a good example of a subheader.
Solution: While you don't want to over-optimize your headers, it's a good idea to include some of your keywords in your headers and sub-headers as appropriate.
9. Body Copy
 Body copy is simply the words on the page.
Body copy is simply the words on the page.
It makes sense that if you want to rank well for your desired keywords, they need to appear in the body copy, which includes all of your paragraphs, lists, and even headers.
One of the bigger mistakes I see when it comes to body copy is what's referred to as “thin content.” A paragraph or two on your products or services just isn't enough to catch Google's attention.
That doesn't mean add a bunch of fluff, either!
It means creating valuable content and backing it up with valuable secondary content. If you're writing an article about how exercise increases memory retention, you might include quotes from memory experts, excerpts from science journals, charts, photos, videos, and more to make the article more valuable to the reader.
If you're just getting started, you may wonder, “exactly how many words should my article be?” There's no magic number, unfortunately. Years ago, people suggested anything over 300 words was effective. But as the quality of content in many industries has gone up, so have the expectations.
According to an article from Snap, for regular content marketing strategies, you should be shooting for 1,000 – 1,500 words, but for heavy hitters, high competition, or definite opportunities, shoot for 2,500 words.
According to a White Board Friday from Moz, there is no perfect length, and you should try and match your length to the needs of your site visitor.
 To paraphrase an old saying, a blog post (or other page) should be like a man's kilt: long enough to cover the subject but short enough to keep your interest.
To paraphrase an old saying, a blog post (or other page) should be like a man's kilt: long enough to cover the subject but short enough to keep your interest.
If you want to do a little research, you could search for a keyword you'd like to rank well for, and see the word count for the top organic results. That might give you a sense of what the competition is like.
Solution: Make sure your keyword is used in the first sentence or two of your page and that you provide enough valuable content that Google will take notice.
10. Images
The standard saying is that search engines can't “see” your images, so you need to use alt-tags–hidden captions–to explain what is in the image.
In the age of facial recognition, I'm not sure if this is entirely true.
However, for the purposes of this article, and to improve your SEO, it's only important to know that you can add additional data to any image on your site. If you're using a platform like WordPress, you can click on an image and easily add this extra information in.
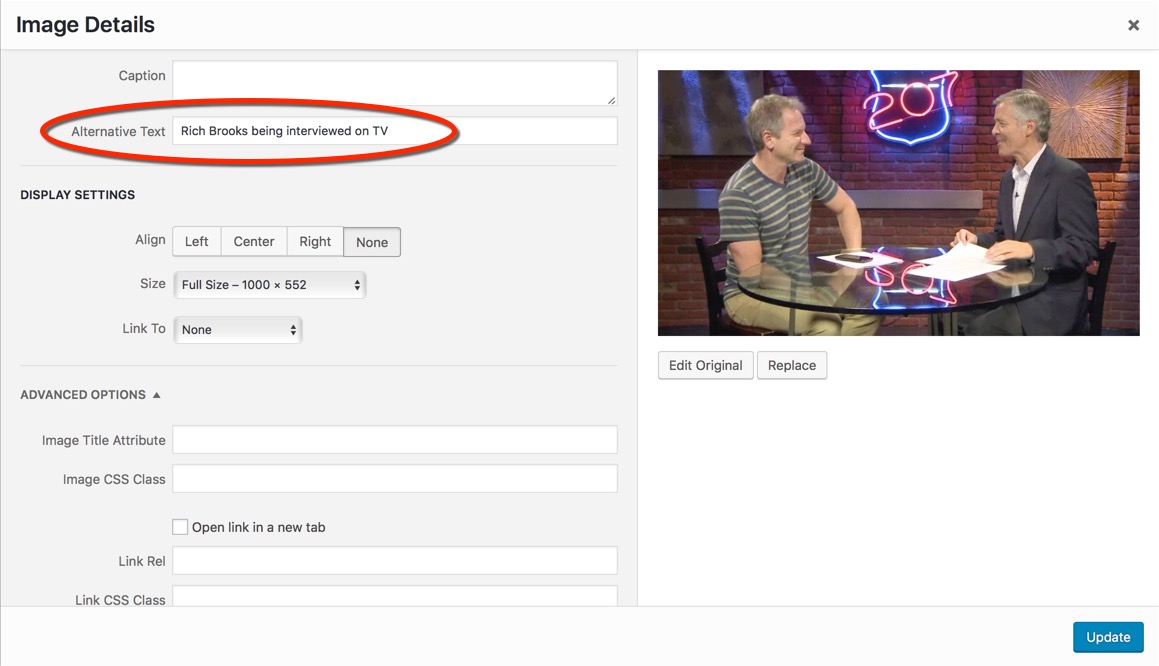
Solution: Give all important images relevant alt-tags. Like all other things in this post, don't over do it.
11. Intrasite links
Click here. Learn more. Continue reading.
These phrases are all missed opportunities when it comes to helping Google understand your website. Search engines look to anchor text–the words in a link–to help them make sense of the page the link points to.
Here's a screen capture from a propane delivery website:
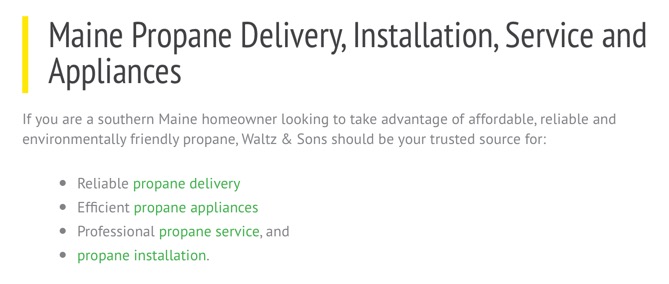
Also, hyperlinked items are more likely to catch your visitor's eye, so better to keep reinforcing the term “propane” rather than the term “click here.”
Solution: As you're linking off to other pages, use the targeted keyword for that page in your link whenever possible, and avoid generic “directional” phrases like “read more.”
Offpage Factors
12. Inbound links
Another way search engines try and evaluate your page is by looking at the quality and quantity of inbound links.
In short, when other websites link to your site, Google sees that as a vote of confidence.
However, like many other SEO tactics, this one has been abused by some webmasters. Because of that, Google may punish you for links from untrustworthy websites, or if the way you acquire links looks artificial or spammy. For example, if you don't have a lot of links and you suddenly get 100 new links over a weekend, that looks suspicious.
Not sure how to avoid angering the SEO gods? Try and get links from relevant websites.
One of my favorite tactics is to do “guest blogging.” That's when you write a post for another blog. You don't get paid for your post, but you do get to link back to your website.
Another good place to get inbound links is from any membership organizations that you belong to. Often, as part of membership, they'll include a link on their website to yours.
There are companies whose business model it is to get inbound links to your website. Beware, however, that not all of them are reputable and can end up hurting your brand and search engine visibility.
You may be wondering how many inbound links you currently have. There's a freemium tool called Open Site Explorer from Moz where you can research how many inbound links you have and other important data. Even if you just use the free version, you can still get some great information.
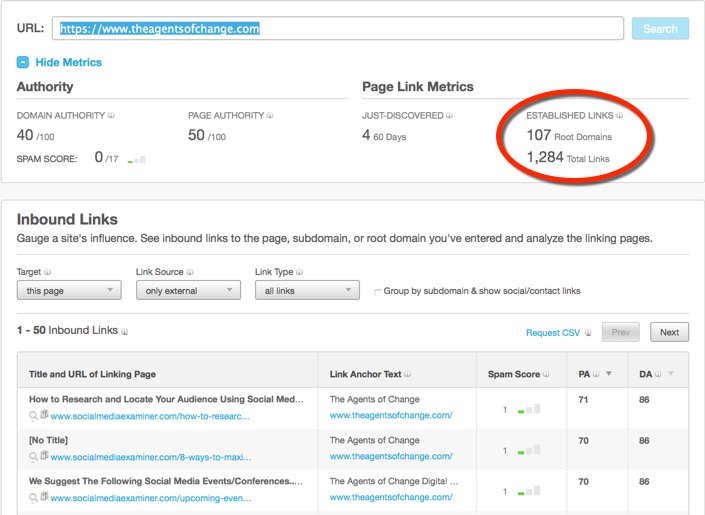
I know what you're wondering: how many inbound links should you have? Well, there's no one right answer, as different industries are going to have different levels of competition.
It's a good exercise to take a look at some of your nearest competitors and use the same tool to find out how many inbound links they have. You can also uncover some of the sites that link to them, reach out to the site owner, and suggest they link to you as well.
Solution: Determine how many inbound links you currently have, and then go about getting incoming links through guest blogging and membership organizations.
Local SEO
13. Optimize your site for local search.
Many businesses, especially SMBs, are “geographically challenged.” A pizza parlor, accountant, or independent gym, is going to get most or all of their business from locals. Similarly, certain businesses may be reliant on tourist dollars, such as a hotel, tour company, or gift shop.
When you do a search for your type of business, do you see results like this?
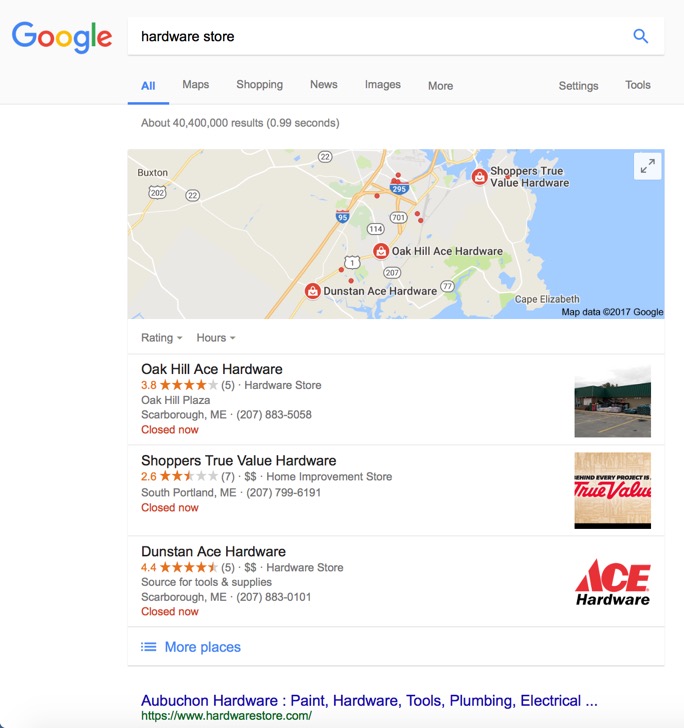
That map, along with the three results is often referred to as the 3 pack. Those are local search results based on where you are or the search you just did.
People can choose one of those three results or click on “More places,” but if Google has done it's job, most people will choose one of the three options above.
In other words, if you want part of this lucrative business, you need to be in the top three results.
While there are a lot of factors that affect Local SEO, one of the most important things you can do is make sure that all of your company information is consistent across the web. To see how you're doing currently, you can check Moz Local which will give you a score from 0 – 100.
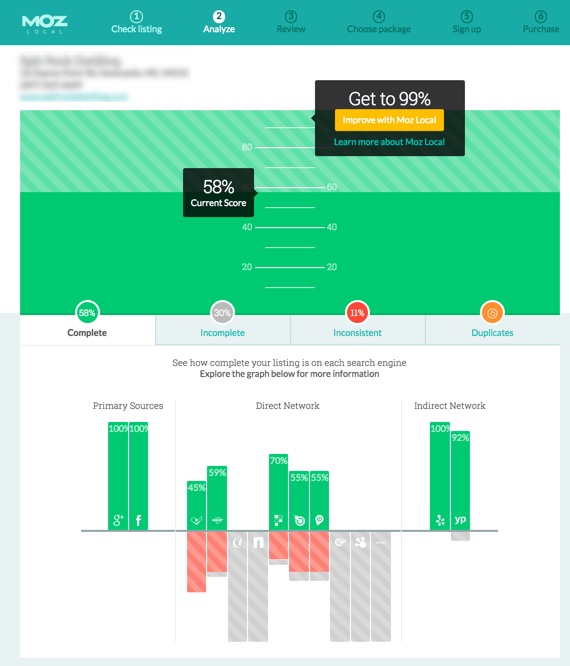
It will also tell you where your information is incorrect, duplicated, or missing so you can fix it.
Solution: Use a tool like Moz Local to see how you're doing in Local Search and improve it!
Next Steps
Just reading this post isn't going to improve your search engine rankings. However, you (possibly with the help of your web developer), should be able to make these changes and start seeing results quickly.
How quickly? Well, if you've never done any SEO before, you might see an improvement in a few days to a couple of weeks. If you're in a competitive industry, it may take quite a bit of time and additional hard work, such as regularly adding new content to your site, actively seeking inbound links, and staying on top of trends in SEO with the help of sites like Search Engine Land, Search Engine Journal, or any of the other resources I've quoted here.
If you're an auditory listener, you might enjoy my digital marketing podcast, which often features SEO topics. Here are a few of my favorite SEO episodes:
- The Rules of Local Search – David Mihm
- How to Beat Your Competition at Google – Jason McGovern
- How to Come Up with Better Keywords for SEO – Rich Brooks
- Why You're Not Ranking Higher at Google – Thom Craver
If you want to download them right to your favorite mobile device or computer, you can subscribe for free at iTunes!
Hopefully, putting this checklist into action will help you improve your search visibility and help you generate more quality leads at your site.
